
For bulk stoichiometric calculations, we are usually determining molar mass, which may also be called standard atomic weight or average atomic mass. This is not the same as molecular mass, which is the mass of a single molecule of well-defined isotopes.
ATOMIC MASS OF C HOW TO
This is how to calculate molar mass (average molecular weight), which is based on isotropically weighted averages. The atomic weights used on this site come from NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology. These relative weights computed from the chemical equation are sometimes called equation weights. In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all of these products together.įormula weights are especially useful in determining the relative weights of reagents and products in a chemical reaction. ECOS 2004 - 17th International Conference on Efficiency, Costs, Optimization, Simulation, and Environmental Impact of Energy on Process Systems. "Optimum design of multi-stage isotope separation process by exergy analysis".

^ "Table of Isotopic Masses and Natural Abundances" (PDF).The isotopes of carbon can be separated in the form of carbon dioxide gas by cascaded chemical exchange reactions with amine carbamate. In 2011, an ab initio calculation of the low-lying states of carbon-12 found (in addition to the ground and excited spin-2 state) a resonance with all of the properties of the Hoyle state. The Hoyle state also is a short-lived resonance with a half-life of 2.4 ×10 −16 s it primarily decays back into its three constituent alpha particles, though 0.0413% of decays (or 1 in 2421.3) occur by internal conversion into the ground state of 12C. This process must occur within 10 −16 seconds as a consequence of the short half-life of 8Be. The Hoyle state is populated when a helium-4 nucleus fuses with a beryllium-8 nucleus in a high-temperature (10 8 K) environment with densely concentrated (10 5 g/cm 3) helium. The existence of the Hoyle state has been confirmed experimentally, but its precise properties are still being investigated. The existence of the 7.7 MeV resonance Hoyle state is essential for the nucleosynthesis of carbon in helium-burning stars and predicts an amount of carbon production in a stellar environment which matches observations. It is produced via the triple-alpha process and was predicted to exist by Fred Hoyle in 1954. The Hoyle state is an excited, spinless, resonant state of carbon-12. The number of moles in 12 grams of carbon-12 became a matter of experimental determination. In 2018, IUPAC specified the mole as exactly 6.022 140 76 × 10 23 "elementary entities". In 1980, the CIPM clarified the above definition, defining that the carbon-12 atoms are unbound and in their ground state. In 1961, the isotope carbon-12 was selected to replace oxygen as the standard relative to which the atomic weights of all the other elements are measured.

This was adopted by the CIPM (International Committee for Weights and Measures) in 1967, and in 1971, it was adopted by the 14th CGPM (General Conference on Weights and Measures). Mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 gram of carbon 12 its symbol is "mol". The two organizations agreed in 1959/60 to define the mole as follows. Carbon-12 is composed of 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons.īefore 1959, both the IUPAP and IUPAC used oxygen to define the mole the chemists defining the mole as the number of atoms of oxygen which had mass 16 g, the physicists using a similar definition but with the oxygen-16 isotope only. Carbon-12 is of particular importance in its use as the standard from which atomic masses of all nuclides are measured, thus, its atomic mass is exactly 12 daltons by definition.
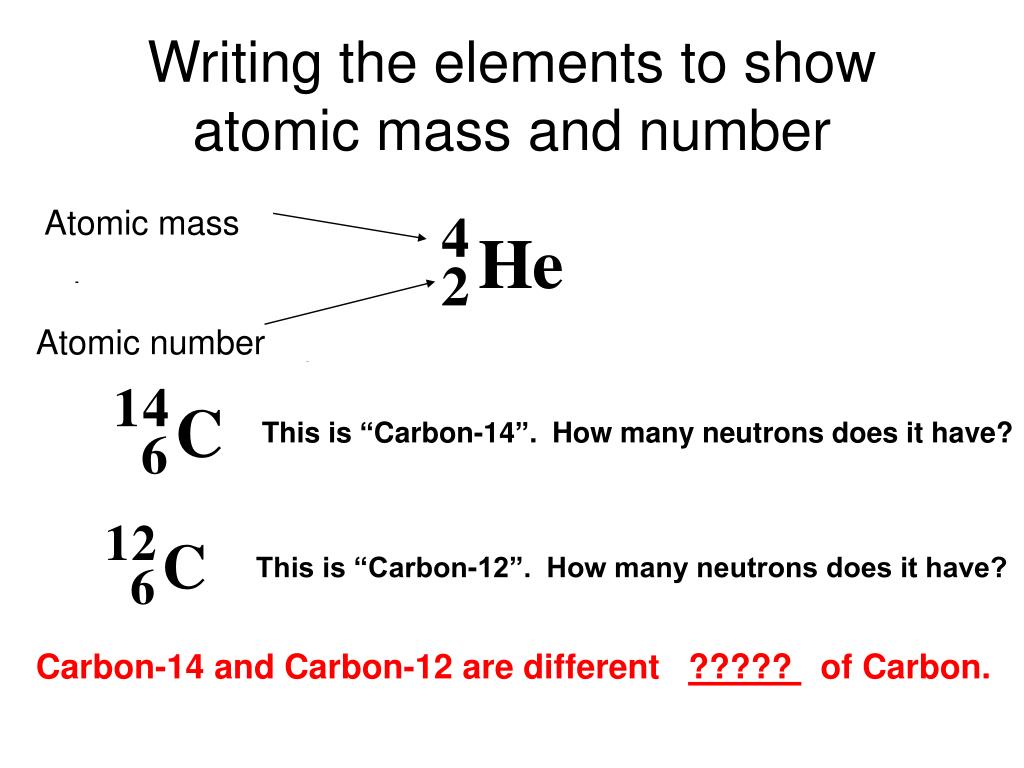
Carbon-12, 12C GeneralĬarbon-12 ( 12C) is the most abundant of the two stable isotopes of carbon ( carbon-13 being the other), amounting to 98.93% of element carbon on Earth its abundance is due to the triple-alpha process by which it is created in stars. For the building in Oregon, see Carbon12.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
